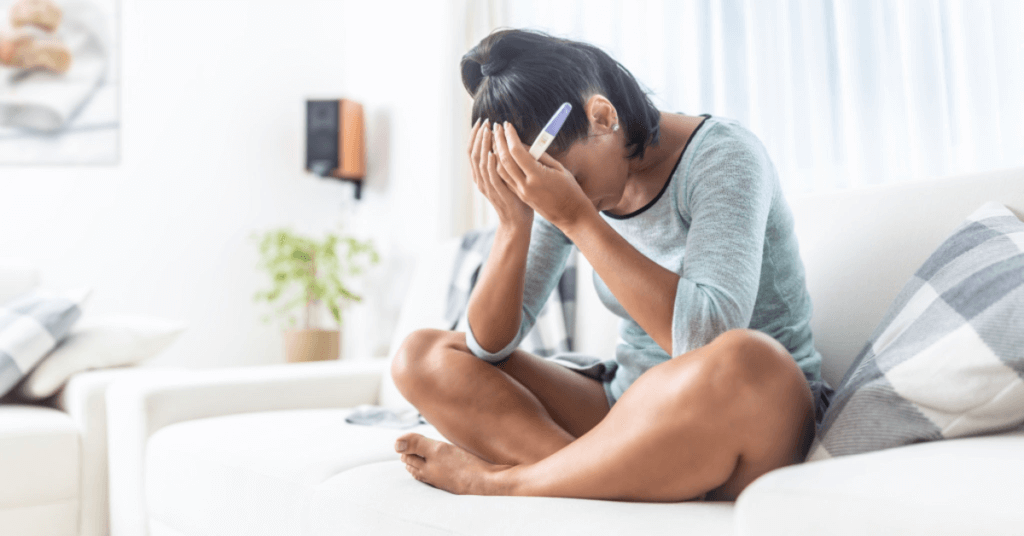
Are you trying to conceive and wondering if there might be something wrong? The signs you can’t get pregnant are not always obvious, but they are crucial in identifying potential fertility issues. Conception is a complex process that requires multiple factors to align, and any sign of difficulty may indicate a problem. It is recommended to consult with a reproductive endocrinologist if you experience challenges in getting pregnant. They can help assess sperm health and sperm counts, which are different reasons for infertility.
Knowing the signs of infertility at the beginning of your journey as a woman can increase your chances of seeking help from a reproductive endocrinologist and finding solutions. Taking steps to address potential fertility issues early on, especially if there are risk factors present, such as age or certain medical conditions, can improve your chances of successful conception. Seeking guidance from a healthcare provider who specializes in fertility care and can assess sperm counts can provide valuable insight and support.
Many people wonder how soon they can get signs of being pregnant or how early these signs might appear. However, it’s important to also understand the risk factors and health information that suggest potential infertility issues, such as sperm health and sperm counts, as this knowledge can help you take proactive steps towards successful conception.
So let’s dive in!
Female Reproductive System and Other Signs of Infertility
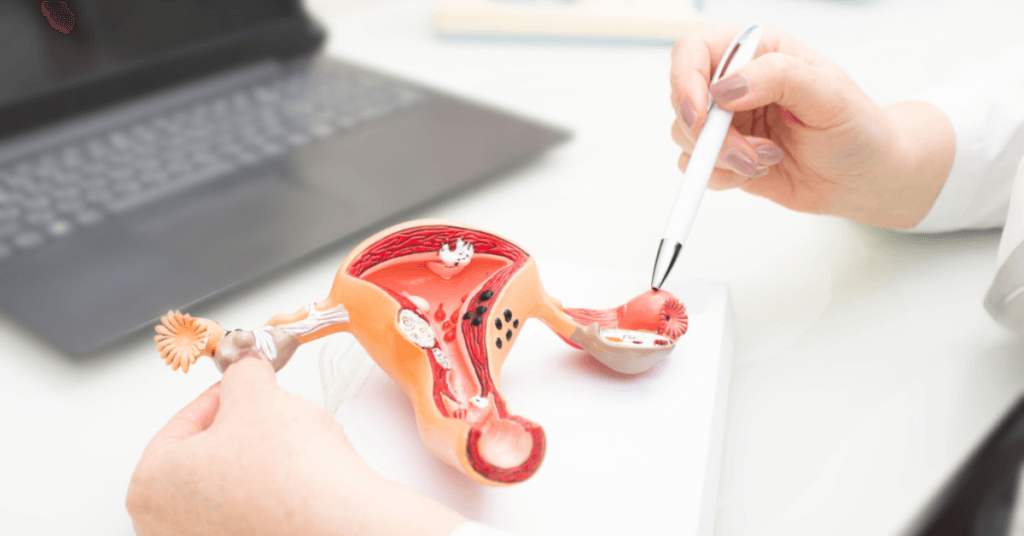
Understanding Female Infertility
Female infertility is a medical condition where a woman is unable to conceive despite having unprotected sex for a year or more. It can be caused by many factors such as hormonal imbalances, structural issues, or lifestyle choices such as obesity. Sperm health and sperm counts also play a crucial role in fertility, and it’s important to seek health information to ensure optimal reproductive health. However, it’s important to note that infertility does not always mean an inability to get pregnant; it can also refer to difficulties carrying a pregnancy to term.
If you are a woman experiencing trouble getting pregnant, it’s essential to see a fertility specialist or reproductive endocrinologist for health information. They will help diagnose and treat female infertility through various methods such as hormone therapy, surgery, or assisted reproductive technologies like IVF. Additionally, they can also evaluate sperm health and sperm counts to determine if male factor infertility is contributing to the difficulty in conceiving.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Female Infertility
There is valuable information regarding several signs and symptoms that indicate female infertility. Some of the most common include:
- Irregular periods are one of the common signs of ovulation problems. If your menstrual cycle is shorter than 21 days or longer than 35 days, it’s important to seek information from a fertility specialist.
- Painful periods: Severe cramping during your period may indicate underlying conditions like endometriosis. If you are experiencing this, it is important to seek information from a fertility specialist as it could be a sign of fertility problems.
- Heavy bleeding: Excessive bleeding during menstruation may suggest uterine fibroids or other structural abnormalities that could lead to fertility problems. For more information, consult with your healthcare provider.
- No periods at all: Amenorrhea (the absence of menstruation) can occur due to hormonal imbalances like PCOS. This information is important for those who may have fertility problems.
It’s important to note that this information about symptoms alone does not necessarily mean you are infertile. However, if you experience any of them for an extended period (more than three months), they warrant further investigation.
Conditions That Affect Female Fertility
Various medical conditions can affect female fertility. Here is some additional information about these conditions:
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is one of the most common hormonal disorders among women of reproductive age. It affects the ovaries’ ability to release eggs regularly, leading to irregular menstrual cycles and difficulty conceiving. PCOS is also associated with insulin resistance, weight gain, and acne. For those seeking more information, there are many resources available to learn about PCOS and its symptoms.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition where the tissue that lines the uterus grows outside of it, causing pain and inflammation. It can also lead to scarring and adhesions that affect fertility by blocking the fallopian tubes or interfering with ovulation.
Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths in the uterus that can cause heavy bleeding, pain, and discomfort. They may also interfere with fertility by blocking the fallopian tubes or altering the shape of the uterus.
Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders like hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid) can disrupt ovulation and menstrual cycles, leading to infertility.
When to See a Doctor
If you have been trying to conceive for a year without success (or six months if you are over 35), it’s time to see a doctor. However, if you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above or have underlying medical conditions that may affect your fertility, you should seek medical attention sooner.
Male and Female Reproductive Systems and Infertility
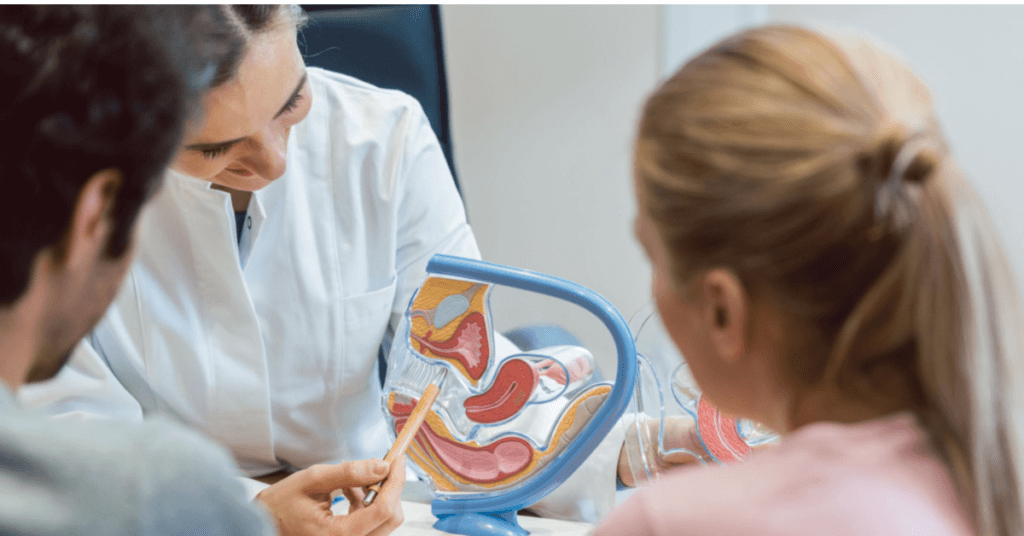
Understanding Male Fertility
Male fertility can be affected by various factors, including age, obesity, and certain medications. As men age, their sperm count decreases, making it more difficult for them to impregnate their partner. Obesity is another factor that affects male fertility as it leads to hormonal imbalances that can affect sperm production. Certain medications such as chemotherapy drugs and anabolic steroids can also cause infertility in men.
Infertility in men can be caused by disorders that affect the testicles, sperm production, and ejaculation. Disorders such as varicocele (enlarged veins in the scrotum) and undescended testicles can lead to low sperm count or poor quality of semen. In some cases, blockages in the ejaculatory ducts can prevent semen from being released during intercourse.
Understanding Female Fertility
Women’s fertility can also be impacted by age, health conditions, and lifestyle factors such as smoking and obesity. As women age, their ovaries produce fewer eggs each month. This makes it harder for them to conceive a child naturally.
Infertility in women can be caused by disorders that affect ovulation, the fallopian tubes, and the uterus. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common condition that affects ovulation in women. Endometriosis is another condition that affects fertility as it causes tissue similar to the lining of the uterus to grow outside of it.
Infertility in Couples
In some cases, infertility in couples may be due to a combination of factors affecting both the male and female reproductive systems. For example, if a man has low sperm count or poor quality semen while his partner has blocked fallopian tubes or endometriosis – this could make conception difficult.
It’s important for couples who are struggling with infertility to seek medical advice from healthcare providers specializing in reproductive health. These healthcare providers can conduct tests to determine the root cause of infertility and provide treatment options.
How is Infertility a Unique Health Challenge for Women of Color?
Infertility is a unique health challenge for women of color due to various factors such as limited access to healthcare, cultural barriers, and racial disparities in healthcare outcomes. According to a study published in the Journal of Women’s Health, African American women are more likely to experience infertility compared to white women. This could be due to higher rates of conditions that affect fertility such as fibroids and PCOS.
There are cultural barriers that prevent women of color from seeking medical help for infertility. In some cultures, infertility is stigmatized and seen as a personal failure rather than a medical condition that requires treatment. This can lead to delays in seeking medical attention or reluctance to pursue fertility treatments.
Moreover, there are racial disparities in healthcare outcomes that affect access to fertility treatments for women of color. Studies show that African American women are less likely to receive fertility treatments compared to white women – even when they have similar levels of infertility.
Age and Fallopian Tube Damage: Causes of Infertility
Fallopian Tubes: The Pathway for Fertilization
The fallopian tubes play a crucial role in the process of conception. These two thin tubes, located on either side of the uterus, are responsible for transporting the egg from the ovary to the uterus. At the same time, they provide a pathway for sperm to reach and fertilize the egg.
However, when something goes wrong with these delicate structures, it can lead to infertility. One of the most common causes of infertility in women is fallopian tube damage.
Age and Its Effects on Fallopian Tubes
As women age, their reproductive systems undergo changes that can affect their ability to conceive. One such change involves the fallopian tubes.
Over time, these tubes may become less flexible and more prone to blockages. This can make it difficult for an egg to travel through them or for sperm to reach the egg. As a result, conception becomes less likely.
In addition to age-related changes, other factors can also contribute to fallopian tube damage.
Infections and Their Impact on Fallopian Tubes
Infections such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can cause scarring and blockages in the fallopian tubes. PID is typically caused by sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea but can also result from other types of bacterial infections.
When left untreated, PID can lead to chronic inflammation that damages the delicate tissues within the reproductive system. Over time, this inflammation can cause permanent scarring that blocks off portions of the fallopian tubes.
Endometriosis: A Common Cause of Fallopian Tube Damage
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to that found in the lining of your uterus grows outside it instead. This tissue growth may occur around your ovaries or even on your fallopian tubes.
As the tissue grows, it can cause inflammation and scarring. This can make your fallopian tubes less flexible, leading to blockages that prevent eggs from reaching your uterus.
Ectopic Pregnancies and Fallopian Tube Damage
In some cases, a fertilized egg may implant itself outside of the uterus. This is known as an ectopic pregnancy. Although rare, ectopic pregnancies can cause significant damage to the fallopian tubes.
When an egg implants itself in the fallopian tube instead of the uterus, it can cause the tube to rupture or burst. This not only damages the tube but also increases the risk of future infertility.
Irregular Menstrual Cycles: A Sign of Infertility
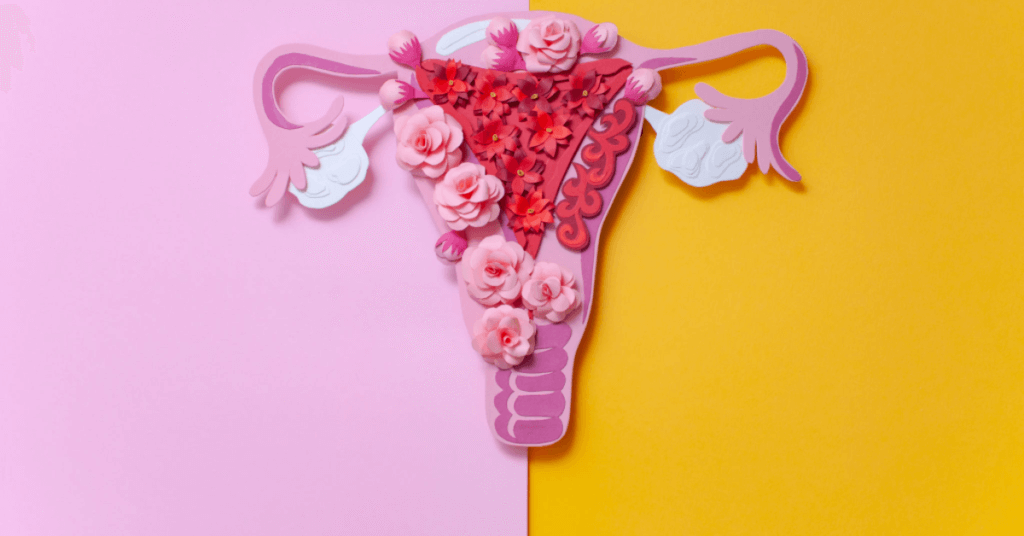

Short or Long Menstrual Cycles Can Indicate a Problem with Ovulation
Irregularity can be a sign of infertility. Menstrual cycles that are shorter than 21 days or longer than 36 days may indicate a problem with ovulation. This means that your body is not releasing an egg every month as it should be, making it difficult for you to become pregnant.
Short menstrual cycles may indicate that the follicular phase of your cycle (the time leading up to ovulation) is too short, which can make it harder for the egg to mature and be released. On the other hand, long menstrual cycles may mean that you have a longer follicular phase, but this can also cause problems with fertility as the egg may not mature properly or at all.
Difficulty Predicting Ovulation Can Make Conception Harder
Women who have irregular periods may have difficulty predicting when they are ovulating, making it harder to conceive. Ovulation typically occurs around day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle, but if your cycles are irregular, this timing can vary greatly from month to month.
There are several methods for tracking ovulation such as basal body temperature monitoring and ovulation predictor kits. However, these methods require regularity in menstrual cycles to accurately predict when ovulation will occur. If you have irregular periods, it can be challenging to track your fertile window and time intercourse accordingly.
Increased Risk of Miscarriage with Irregular Periods
Irregular periods can also increase the risk of miscarriage if pregnancy does occur. This is because irregular periods often indicate hormonal imbalances or issues with ovulation which can lead to an unhealthy pregnancy.
If you do become pregnant with irregular periods, it is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to monitor hormone levels and ensure that the pregnancy is progressing as it should be. In some cases, medication or other interventions may be necessary to support a healthy pregnancy.
Talking to Your Doctor About Irregular Periods
If you have irregular periods, it is important to talk to your doctor about possible causes and treatment options. There are several factors that can contribute to irregular menstrual cycles such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, or weight fluctuations.
Your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight or reducing stress levels. They may also prescribe medication or hormone therapy to regulate your menstrual cycle and improve fertility.
Painful, Heavy, or Long Periods: Can You Still Be Infertile?
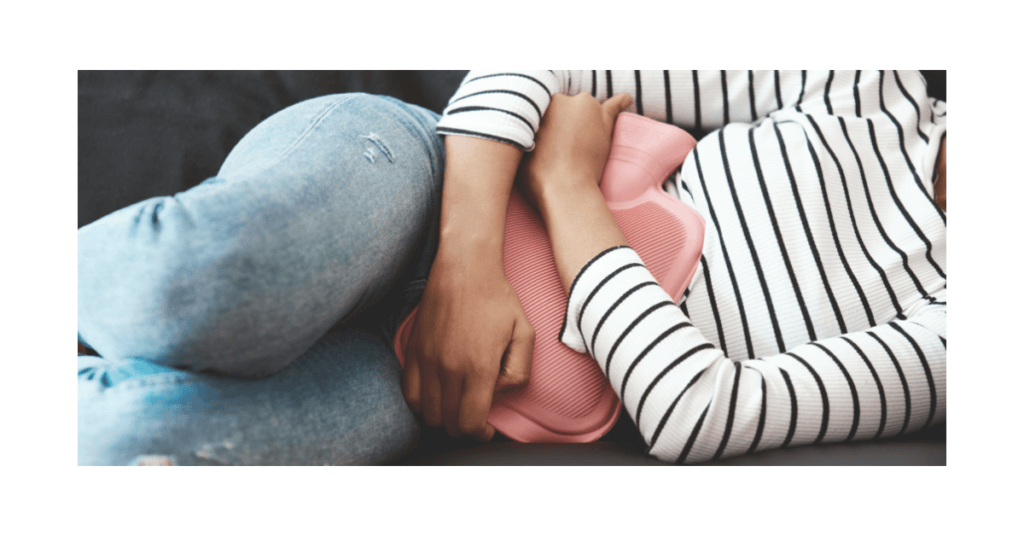

Painful Periods and Their Connection to Fertility
Painful periods are a common problem that affects many women. However, did you know that they can also be a sign of endometriosis, which can impact fertility? Endometriosis is a condition where the tissue lining the uterus grows outside of it, causing inflammation and pain.
Endometriosis can affect fertility in several ways. First, the inflammation caused by this condition can damage the eggs or sperm before they even have a chance to meet. Second, endometrial tissue growth around the ovaries or fallopian tubes can prevent them from functioning properly. Lastly, scarring caused by endometriosis may make it difficult for an egg to travel down the fallopian tube and implant in the uterus.
If you experience painful periods regularly, especially if they are accompanied by other symptoms such as heavy bleeding or pain during sex, it’s essential to speak with your doctor. They may recommend medication or surgery to manage your symptoms and improve your chances of conceiving.
Heavy Periods and Their Impact on Fertility
Heavy periods may indicate uterine fibroids or polyps that can interfere with conception. Fibroids are non-cancerous growths in the uterus that can cause heavy bleeding and pain during menstruation. Polyps are small growths on the lining of the uterus that can also cause heavy bleeding.
Both fibroids and polyps can interfere with conception by preventing fertilization or implantation of an embryo. They may also increase your risk of miscarriage if you do become pregnant.
If you’re experiencing heavy periods regularly or notice changes in your menstrual flow pattern, make sure to talk to your doctor about it. They may recommend medication or surgery to manage these conditions and improve your chances of getting pregnant.
Irregular Periods and Their Impact on Fertility
Irregular periods or missed periods for several months may suggest ovulation problems. Ovulation is the release of an egg from the ovaries, which must occur for conception to happen.
If you’re not ovulating regularly, it can be challenging to get pregnant. Factors that can impact ovulation include stress, weight changes, hormonal imbalances, and certain medical conditions.
If you’re experiencing irregular periods or have missed several periods in a row, make sure to talk to your doctor about it. They may recommend lifestyle changes or medication to regulate your menstrual cycle and improve your chances of getting pregnant.
Weight Gain/Loss and Its Effect on Fertility
Sudden weight gain or loss can disrupt hormonal balance and affect ovulation. Hormonal imbalances can cause irregular periods or prevent ovulation altogether.
Excessive weight gain can also lead to insulin resistance, which can interfere with ovulation. On the other hand, extreme weight loss can lead to low body fat levels that reduce estrogen production in the body.
If you’ve experienced sudden weight changes recently and are having trouble conceiving, make sure to talk to your doctor about it. They may recommend making dietary changes or starting an exercise routine to help regulate your hormones and improve your chances of getting pregnant.
Seeking Medical Advice for Menstrual Issues
It’s essential to seek medical advice if you’re experiencing any menstrual issues that could impact fertility. Your doctor may recommend medication or surgery depending on the severity of your condition.
In some cases, lifestyle changes such as losing weight or reducing stress levels may be enough to improve fertility. However, it’s essential not to delay seeking help since early intervention is often key when dealing with fertility issues.
Pelvic Pain and Pain During Sex: Signs You Can’t Get Pregnant

Pelvic Pain can be a Sign that You Can’t Get Pregnant
Pelvic pain is a common symptom among women, but it can also be an indication of infertility issues. If you experience persistent pelvic pain, it’s crucial to seek medical advice as soon as possible.
Several conditions can cause pelvic pain and affect fertility. One of the most common causes of pelvic pain is endometriosis, a condition where the tissue that lines the uterus grows outside of it. This abnormal growth can lead to inflammation, scarring, and adhesions in the pelvis, which may interfere with ovulation and fertilization.
Other factors that may contribute to pelvic pain include ovarian cysts or tumors, fibroids (benign growths in the uterus), and adenomyosis (a condition where endometrial tissue grows into the muscular wall of the uterus). These conditions may also affect fertility by altering hormone levels or interfering with implantation.
If you’re experiencing pelvic pain along with other symptoms like heavy bleeding during periods or painful bowel movements, it’s essential to discuss these symptoms with your doctor. They may recommend further testing or refer you to a specialist for treatment.
Pain During Sex May Indicate Infertility Issues
Pain during sex (also known as dyspareunia) is another sign that you may have trouble getting pregnant. Dyspareunia affects up to 20% of women at some point in their lives and can have many causes.
One common cause of dyspareunia is vaginal dryness, which can occur due to hormonal changes or certain medications. Without adequate lubrication, intercourse can be painful and uncomfortable.
Another potential cause of dyspareunia is an infection or inflammation in the reproductive organs. Conditions like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can cause swelling and irritation in the cervix, uterus, or fallopian tubes. This inflammation can make sex painful and may also interfere with fertility by blocking the passage of sperm.
Endometriosis can also cause pain during sex, as well as other symptoms like heavy periods and infertility. If you have endometriosis, the tissue that normally lines your uterus grows outside of it, which can cause inflammation and scarring in the pelvis. These adhesions may make intercourse painful or difficult and can also affect fertility by interfering with ovulation or implantation.
If you’re experiencing pain during sex, it’s important to talk to your doctor about your symptoms. They may recommend further testing or refer you to a specialist for treatment.
Seeking Medical Advice is Crucial if You Experience Pelvic Pain or Pain During Sex
If you’re experiencing pelvic pain or pain during sex, it’s essential to seek medical advice as soon as possible. These symptoms could be an indication of underlying health issues that require prompt treatment.
Your doctor will likely perform a physical exam and may recommend additional tests like blood work, ultrasounds, or laparoscopy (a minimally invasive surgical procedure). Based on your diagnosis, they’ll develop a treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Treatment for pelvic pain or dyspareunia depends on the underlying cause but may include medications like antibiotics or hormonal therapy. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove growths like fibroids or endometrial tissue.
Ejaculation or Ejaculate Issues: Signs of a Fertility Problem

Low Sperm Counts Can Be a Sign of Fertility Issues
If you and your partner have been trying to conceive for over a year without success, it may be time to consider that there could be an underlying fertility issue. One common cause of infertility in men is low sperm count. A healthy sperm count ranges from 15 million to more than 200 million sperm per milliliter of semen. If the number falls below this range, it can make conception difficult.
Low sperm count can be caused by a variety of factors such as hormonal imbalances, infections, physical abnormalities, and lifestyle factors like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. It’s important to speak with your doctor if you suspect that you may have low sperm count or any other fertility issues.
Ejaculation Problems Can Cause Fertility Problems
Ejaculation problems are another common cause of male infertility. Retrograde ejaculation is one type where semen flows back into the bladder instead of out through the penis during ejaculation. This condition can be caused by certain medications or medical conditions like diabetes. Another type is premature ejaculation which occurs when a man ejaculates before he or his partner would like during sexual intercourse.
Other ejaculation issues include delayed ejaculation where it takes longer than usual for a man to ejaculate or absent ejaculation where no semen is released during orgasm. These problems can also lead to fertility issues as they affect the ability for sperm to reach the egg.
Abnormalities in Sperm Shape or Motility Can Affect Sperm Health and Lead to Fertility Problems
Sperm motility refers to how well and quickly the sperm move towards the egg. If there are abnormalities in shape or motility, it can make conception difficult as they will not be able to swim effectively towards the egg. Poor motility can also increase the risk of miscarriage if fertilization does occur.
Sperm shape is also important for fertility. If there are abnormalities in the shape of the sperm, it can affect their ability to fertilize an egg. For example, if the sperm head is too large or misshapen, it may not be able to penetrate the egg’s outer layer.
Infections or Inflammation in The Reproductive System Can Cause Problems with Ejaculation or Affect Sperm Health
Infections and inflammation in the reproductive system can also cause fertility problems. Sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea can lead to scarring and blockages in the reproductive tract which can make conception difficult. Inflammation of the prostate gland (prostatitis) can also affect sperm health and cause ejaculation problems.
It’s important to practice safe sex and get tested regularly for sexually transmitted infections if you are trying to conceive. If you suspect that you may have an infection or inflammation, speak with your doctor as soon as possible.
Certain Medications or Medical Treatments Can Also Affect Ejaculation or Sperm Health, Leading to Fertility Issues
Certain medications like antidepressants, antihistamines, and blood pressure medications can affect ejaculation or sperm health leading to fertility issues. Chemotherapy and radiation treatments used for cancer treatment can also damage sperm production leading to infertility.
If you are taking any medication or undergoing medical treatments, speak with your doctor about how they may affect your fertility before trying to conceive.
Fertility Problems Can Also Be Caused by Issues with The Egg Such as Ovulation Disorders Or Blockages in The Fallopian Tubes

Fertility issues aren’t just limited to men; women can experience them too. One common cause of female infertility is ovulation disorders where eggs aren’t released regularly from the ovaries. This can be caused by hormonal imbalances, stress, excessive exercise, and being underweight or overweight.
Blockages in the fallopian tubes can also cause fertility problems as they prevent the egg from meeting sperm. This can be caused by infections, endometriosis, or scar tissue from previous surgeries.
Common Causes of Infertility: Male Infertility and Uterine or Cervical Issues
Male Infertility: Different Reasons for Low Sperm Count, Poor Sperm Motility, or Abnormal Sperm Shape
Infertility is a common problem affecting millions of couples worldwide. While both male and female factors contribute to infertility, male infertility accounts for approximately 40% of all cases. Male infertility occurs when there are problems with the quality, quantity, or movement of sperm. Some of the most common causes of male infertility include:
- Hormonal imbalances: The hypothalamus and pituitary glands in the brain produce hormones that regulate testosterone production and sperm development. Any disruption in this hormonal balance can lead to low sperm count or poor sperm motility.
- Genetic factors: Certain genetic conditions such as Klinefelter syndrome, Y chromosome deletions, and cystic fibrosis can affect the production or function of sperm.
- Lifestyle choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, exposure to environmental toxins like pesticides and chemicals can all impact sperm quality.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions like diabetes, hypertension, infections like mumps orchitis can also affect fertility.
If you suspect male infertility may be an issue for you and your partner’s inability to conceive a child naturally, it’s essential to speak with a healthcare provider who specializes in reproductive medicine. They may recommend various treatments depending on the underlying cause of infertility.
Uterine Issues: Hormonal Imbalances and Previous Surgeries Can Cause Fibroids, Polyps or Adhesions
Uterine issues are another common cause of infertility in women. These issues prevent implantation from occurring when fertilization happens by preventing the fertilized egg from attaching itself to the uterine lining. Here are some common causes of uterine issues:
- Hormonal imbalances: An imbalance between estrogen and progesterone levels can cause abnormal growths in the uterus, such as fibroids or polyps.
- Previous surgeries: Surgeries like cesarean sections, myomectomies, and dilation and curettage (D&C) procedures can cause adhesions or scarring that interfere with implantation.
Uterine issues can be diagnosed through various tests like ultrasounds, hysterosalpingography, and hysteroscopy. Treatment options depend on the severity of the condition. Hormonal imbalances may be treated with medications to regulate hormone levels, while surgical intervention may be necessary for more severe cases.
Cervical Issues: Infections and Structural Abnormalities Can Make it Difficult for Sperm to Reach the Egg
Cervical issues are another common cause of infertility in women. The cervix is a small opening at the bottom of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It produces mucus that helps sperm travel through it to reach an egg for fertilization. Here are some common causes of cervical issues:
- Mucus abnormalities: The cervix produces mucus at different stages of a woman’s menstrual cycle, which changes consistency based on hormonal fluctuations. Any abnormalities in this process can make it challenging for sperm to pass through.
- Cervical stenosis: This condition occurs when the cervix is too narrow or blocked, making it difficult for sperm to pass through.
- Infections: Sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea can cause inflammation and scarring in the cervix that affects fertility.
Cervical issues can be diagnosed through various tests like ultrasounds and hysteroscopy. Treatment options depend on the severity of the condition but may include antibiotics or surgical intervention.
History of Cancer or STIs as a Factor in Infertility
A history of cancer can increase the risk of infertility in both men and women.
Cancer is a devastating disease that can affect many aspects of a person’s life, including their fertility. Certain types of cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy, can damage the reproductive system and decrease the chances of conceiving a child. For women, cancer treatment can cause damage to the ovaries, which may lead to premature menopause or ovarian failure. Men may experience a decrease in sperm count or quality after undergoing cancer treatment.
However, not all types of cancer treatments have the same impact on fertility. Some patients may be able to preserve their fertility by freezing eggs or sperm before undergoing treatment. Others may choose to delay treatment until after they have had children. It is important for individuals with a history of cancer who wish to have children to discuss their options with their healthcare provider.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia and gonorrhea can cause infertility by damaging the reproductive system.
STIs are common infections that are spread through sexual contact. If left untreated, these infections can cause serious health problems, including infertility. Chlamydia and gonorrhea are two STIs that commonly cause infertility by damaging the reproductive system.
In women, chlamydia and gonorrhea can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which is an infection of the reproductive organs that can cause scarring and blockages in the fallopian tubes. This makes it difficult for sperm to reach an egg for fertilization. In men, these infections can cause inflammation of the testicles or prostate gland, which may lead to decreased sperm production or blockages in the reproductive tract.
Fortunately, most STIs are treatable with antibiotics if caught early enough. It is important for sexually active individuals to get tested regularly for STIs and to practice safe sex to prevent the spread of infection.
Inflammatory diseases, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), can also increase the risk of infertility.
In addition to STIs, other inflammatory diseases can also increase the risk of infertility. PID is one example of an inflammatory disease that affects the reproductive system. It occurs when bacteria from the vagina or cervix travel up into the uterus and fallopian tubes, causing inflammation and scarring.
PID can cause blockages in the fallopian tubes, making it difficult for sperm to reach an egg for fertilization. Women with PID may also experience chronic pain or discomfort during sex. If left untreated, PID can lead to serious health problems, including infertility and ectopic pregnancy.
Treatment for PID typically involves a course of antibiotics to clear up the infection. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove scar tissue or repair damage to the reproductive organs.
It is important to seek health information and treatment for these risk factors to prevent infertility.
If you have a history of cancer or have been diagnosed with an STI or inflammatory disease, it is important to seek medical treatment as soon as possible. Early detection and treatment can help prevent long-term complications such as infertility.
It is also important to take steps to protect your reproductive health. This includes practicing safe sex by using condoms and getting tested regularly for STIs if you are sexually active. Women should also consider getting regular gynecological exams and Pap tests to screen for cervical cancer.
By taking these steps, you can help ensure that you maintain your fertility and overall reproductive health.
Personalized Care and Focus on Overall Health

Mayo Clinic’s approach to treating infertility involves personalized care and a focus on the patient’s overall health. The clinic’s doctors recognize that infertility can be a stressful and emotional experience for couples, so they provide compassionate care throughout the treatment process.
In addition to medical treatments, Mayo Clinic also offers resources such as counseling services and support groups to help patients cope with the emotional aspects of infertility.
The clinic’s focus on overall health is also important in increasing the chances of successful treatment. Doctors work with patients to address lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and stress management that may affect fertility.
Understanding the Signs You Can’t Get Pregnant
If you’re struggling to conceive, it’s important to understand the signs that may indicate infertility. There are various factors that can impact fertility, ranging from reproductive system issues to age and lifestyle choices.
Female reproductive system problems such as irregular menstrual cycles, heavy or painful periods, and pelvic pain during sex can all be signs of infertility. Fallopian tube damage and a history of cancer or STIs can also affect a woman’s ability to get pregnant.
Male infertility is also a common issue and can be caused by ejaculation or ejaculate issues, as well as uterine or cervical problems in female partners. Age is another factor that affects both male and female fertility, with older individuals experiencing more difficulty conceiving.
It’s important to seek medical advice if you’re experiencing any of these signs of infertility. Treatment options may include medication, surgery, or assisted reproductive technologies like IVF.
FAQs:
Q1: What lifestyle factors can impact fertility?
A1: Lifestyle choices such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and being overweight can all negatively impact fertility.
Q2: How long should I try to conceive before seeking medical advice?
A2: If you’re under 35 years old and have been trying for over a year without success, it’s recommended that you seek medical advice. For those over 35 years old, six months of trying without success is cause for concern.
Q3: Can stress affect my ability to get pregnant?
A3: While stress alone isn’t a direct cause of infertility, it can impact hormone levels and ovulation cycles which may make conception more difficult.
Q4: Is there anything I can do at home to improve my chances of getting pregnant?
A4: Maintaining a healthy diet and weight, reducing stress levels through relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation, and tracking ovulation cycles using ovulation kits can all improve your chances of conceiving.
Q5: Are there any alternative treatments for infertility?
A5: Some alternative therapies like acupuncture and herbal supplements may be beneficial in improving fertility, but it’s important to consult with a medical professional before trying any alternative treatments.
Q6: How much does fertility treatment cost?
A6: The cost of fertility treatment varies depending on the type of treatment needed and your location. On average, IVF can cost anywhere from $12,000 to $15,000 per cycle.
Q7: Is infertility more common in men or women?
A7: Infertility affects both men and women equally, with each gender contributing to approximately 30-40% of infertility cases.