Miscarriage, also known as pregnancy loss, is a devastating event that occurs during the gestation period. It can be caused by various medical conditions, including partial molar pregnancy. Understanding why miscarriages happen and finding ways to cope with the emotional toll it takes is essential for those who have experienced this loss.
Miscarriage, also known as the loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks, can occur due to various medical conditions during gestation. This unfortunate event leaves parents-to-be in a state of shock and grief. It’s estimated that 10-20% of known pregnancies end in miscarriage, making it more common than most people realize.
There are various causes behind recurrent miscarriage, also known as early pregnancy loss. Chromosomal abnormalities, such as in cases of complete miscarriage or partial molar pregnancy, often play a significant role. Maternal health conditions, such as diabetes or thyroid disorders, can also increase the risk.
Dealing with early pregnancy loss, such as a miscarriage or partial molar pregnancy, is an emotional rollercoaster for people in the first few weeks. The support from loved ones becomes crucial during these times of pain and confusion. Seeking medical advice is equally important to ensure proper care and understanding.
When faced with the loss of a pregnancy, many individuals search online for information and support. That’s why we’ve created this web page – to provide you with information about miscarriages, including their causes, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and support for medical conditions related to pregnancy.
So if you or someone you know has experienced early pregnancy loss or a molar pregnancy, rest assured that you’re not alone. We’re here to guide you through the complexities of miscarriage – offering support when words feel wrong and hope seems lost. Our pregnancy care providers are here for you during this difficult time, providing the care and guidance you need in the coming weeks.
Let us help you navigate this difficult terrain of recurrent miscarriage so that you can find comfort amidst the stormy seas of grief. Consult with an ed pregnancy care provider or doctor for guidance.

Causes of Miscarriage: Exploring Risk Factors
Advanced Maternal Age: A Higher Chance of Miscarriage
One significant risk factor for miscarriage is advanced maternal age. As women get older, the chances of experiencing a spontaneous abortion increase. This is because as women age, the quality of their eggs decreases, making them more prone to genetic abnormalities. These abnormalities can lead to pregnancy loss and increase the risk of miscarriage. So, if you’re planning to conceive later in life, it’s crucial to be aware of this increased risk and consult with your doctor for appropriate guidance.
Chronic Health Conditions: Contributing Factors
Another factor that can contribute to miscarriages is the presence of chronic health conditions such as diabetes or thyroid disorders. These conditions affect the body’s hormonal balance and overall well-being, potentially impacting the development and maintenance of a healthy pregnancy. For instance, uncontrolled diabetes can lead to complications that may result in a higher risk of miscarriage. It is essential for individuals with pre-existing health conditions to work closely with their doctor to manage these conditions effectively before attempting pregnancy.
Lifestyle Choices: Influence on Miscarriage Risk
Certain lifestyle factors, such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug use, can increase the risk of miscarriage. The toxins present in cigarettes and substances like alcohol or drugs can negatively impact fetal development and increase the likelihood of a miscarriage occurring. Therefore, it’s vital for individuals who are trying to conceive or are already pregnant to avoid these harmful habits and prioritize their own health as well as that of their unborn child. It is recommended to consult a doctor for further guidance.
Infections, Hormonal Imbalances, and Uterine Abnormalities
Infections within the reproductive system can pose a risk for miscarriages too. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia or gonorrhea can cause inflammation in the uterus or fallopian tubes, leading to complications that may result in pregnancy loss. Hormonal imbalances can disrupt the delicate reproductive processes necessary for a successful pregnancy. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders can affect hormone levels and increase the risk of miscarriage. Furthermore, uterine abnormalities like fibroids or structural issues can interfere with implantation and fetal development, potentially resulting in miscarriage. It is important to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Genetic Factors: A Role in Miscarriage Risk
Genetic issues in either parent can significantly increase the risk of miscarriage. Certain genetic conditions or chromosomal abnormalities can be inherited and passed on to the offspring, increasing the chance of pregnancy loss. It’s essential for couples with a family history of genetic disorders or recurrent miscarriages to consult with a doctor before attempting to conceive. This way, they can better understand their risks and explore available options for minimizing those risks.
Understanding the various causes of miscarriage is crucial for individuals planning to start or expand their families. Advanced maternal age, chronic health conditions, lifestyle choices, infections, hormonal imbalances, uterine abnormalities, and genetic factors all contribute to the overall risk of experiencing a miscarriage. By being aware of these potential risks and taking appropriate measures such as maintaining good health habits and seeking medical advice from a doctor when needed, individuals can increase their chances of having a healthy pregnancy and reducing the likelihood of pregnancy loss.
So remember: take care of yourself physically and mentally by consulting with a doctor, especially if you have concerns about ed, while also considering your partner’s well-being when planning for parenthood!

Signs and Symptoms: Recognizing Early Warning Signs
Vaginal bleeding or spotting is a common symptom of early miscarriage.
One of the most common signs that something might be wrong with a pregnancy is vaginal bleeding or spotting. It’s important to note that not all bleeding during pregnancy indicates a miscarriage, as some light spotting can occur without any complications. However, if you experience heavy bleeding or bright red blood, it could be a cause for concern. The amount and duration of bleeding can vary from person to person, but it’s essential to seek medical attention if you notice any abnormal bleeding.
Cramping or abdominal pain may occur alongside bleeding during a miscarriage.
In addition to vaginal bleeding, cramping or abdominal pain is another sign that may accompany a miscarriage. These cramps can range from mild discomfort to severe pain and are often similar to menstrual cramps. If you experience persistent or worsening pain in your abdomen along with bleeding, it’s crucial to consult your healthcare provider immediately. They will be able to assess your condition and provide appropriate guidance based on your symptoms.
Loss of pregnancy symptoms like breast tenderness or morning sickness could indicate a problem.
Pregnancy comes with its fair share of symptoms, such as breast tenderness and morning sickness. However, if you notice that these symptoms suddenly disappear or significantly decrease in intensity, it could be an indication of a potential problem, including miscarriage. While the loss of pregnancy symptoms alone does not definitively confirm a miscarriage, it is worth discussing with your healthcare provider for further evaluation and reassurance.
Passing tissue or clots from the vagina is another sign that a miscarriage may be occurring.
A significant sign of a possible miscarriage is passing tissue or blood clots from the vagina. This can happen alongside vaginal bleeding and often indicates that the body is expelling fetal tissue. It’s important to understand that passing tissue does not always mean a miscarriage has occurred, as some women may experience other conditions like an ectopic pregnancy or molar pregnancy. Nevertheless, if you observe the passing of tissue or clots, it is crucial to reach out to your healthcare provider for proper evaluation and guidance.
If you experience any signs or symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly.
Regardless of the specific signs and symptoms you experience, it is vital to seek immediate medical attention if you suspect a miscarriage. Only a healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and determine the appropriate course of action based on your individual circumstances. They will likely conduct tests such as ultrasound scans and blood work to assess your condition thoroughly. Remember that early detection and intervention can make a significant difference in managing complications associated with miscarriage.
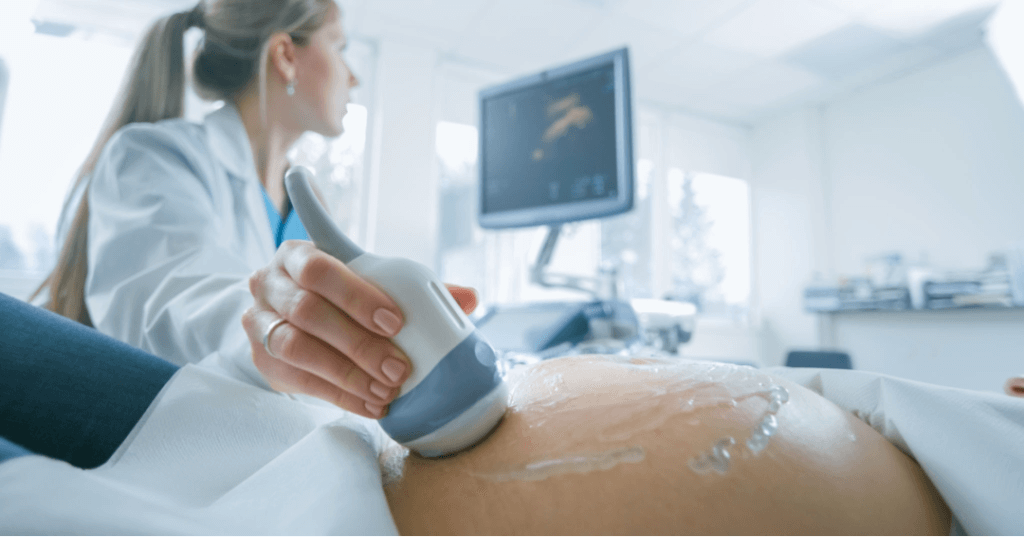
Diagnosing Miscarriage: Tests and Procedures
Ultrasound Scans: Checking for Fetal Heartbeat Absence
One of the most common methods used to diagnose a miscarriage is through ultrasound scans. This non-invasive procedure allows healthcare providers to examine the uterus and check for the absence of a fetal heartbeat. During an ultrasound, a handheld device called a transducer is moved over the abdomen or inserted into the vagina to create images of the uterus and its contents.
If a pregnancy has reached a stage where a heartbeat should be detectable, but none is found during the ultrasound, it may indicate a miscarriage. However, it’s important to note that in some cases, especially during early pregnancy, it may be challenging to detect a fetal heartbeat with certainty. In such situations, additional tests or follow-up ultrasounds might be necessary for confirmation.
Blood Tests: Measuring Hormone Levels (hCG)
Another way to determine if a pregnancy is progressing normally or if a miscarriage has occurred is through blood tests that measure hormone levels, specifically human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). hCG is produced by cells in the placenta and can provide valuable insights into the health of an ongoing pregnancy.
In cases of miscarriage, hCG levels often decline instead of increasing as expected during early pregnancy. By monitoring these hormone levels over time, healthcare providers can assess whether there are any abnormalities indicating potential complications or miscarriage.
Dilation & Curettage (D&C) Procedure: Removing Remaining Tissue
When a miscarriage occurs naturally or if medically/surgically induced abortion fails completely, there may be remaining tissue in the uterus that needs to be removed. In such cases, healthcare providers may recommend a procedure called dilation and curettage (D&C).
During this procedure, the cervix is dilated (widened), allowing access to the uterine cavity. A curette, a thin instrument with a sharp edge, is then used to gently scrape and remove the remaining tissue. D&C is typically performed under anesthesia and can help ensure that all pregnancy-related tissue has been removed, reducing the risk of complications such as infection.
Hysteroscopy: Examining the Uterine Cavity
In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend a hysteroscopy to examine the uterine cavity more closely. This procedure involves inserting a thin tube with a lighted camera through the cervix into the uterus. By visualizing the uterine lining directly, healthcare providers can identify any abnormalities or potential causes of miscarriage.
Hysteroscopy allows for a detailed assessment of the uterine cavity’s structure and helps determine if there are any growths (such as polyps or fibroids) that might interfere with implantation or pregnancy progression. It can also identify any scarring or adhesions within the uterus that could lead to recurrent miscarriages.
Genetic Testing of Fetal Tissue: Gaining Insights into Potential Causes
Genetic testing of fetal tissue can provide valuable insights into potential causes of miscarriage. When a miscarriage occurs, healthcare providers may suggest analyzing the fetal tissue for chromosomal abnormalities or other genetic factors that could have contributed to its demise.
This testing helps determine whether there were any specific genetic conditions present in the fetus that may have hindered normal development. Understanding these underlying genetic factors can be crucial for the pregnancy care provider in providing appropriate counseling and guidance for future pregnancies.

Treatment Options: Addressing Emotional and Physical Needs
In cases of incomplete miscarriage, a D&C procedure may be performed by a pregnancy care provider to remove remaining tissue.
If you experience an incomplete miscarriage, your healthcare provider may recommend a procedure called dilation and curettage (D&C). This is a common medical intervention that involves dilating the cervix and removing any remaining pregnancy tissue from the uterus. The procedure is usually done under general anesthesia to minimize discomfort.
During a D&C, your healthcare provider will carefully scrape or suction out the remaining tissue from the uterine lining. This helps ensure that all pregnancy-related material is removed, reducing the risk of infection and other complications. While it can be emotionally challenging to undergo this procedure, it is an effective way to address physical needs after a miscarriage.
Medication may be prescribed to help the body expel the pregnancy tissue during a miscarriage.
In some cases, medication may be recommended as an alternative to surgery for managing a miscarriage. Your healthcare provider might prescribe medications like misoprostol or mifepristone, which work by stimulating contractions in the uterus to help expel any remaining pregnancy tissue.
These medications are typically taken orally or inserted vaginally and can cause cramping and bleeding similar to heavy menstrual periods. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions closely when using these medications and seek medical attention if you experience severe pain or excessive bleeding.
Emotional support from a pregnancy care provider through counseling or support groups can aid in coping with grief and loss.
Experiencing a miscarriage can be emotionally devastating. It’s normal to feel grief, sadness, anger, or guilt following such a loss. Seeking emotional support through counseling or joining support groups specifically designed for individuals who have experienced pregnancy loss can provide comfort during this difficult time.
Counseling sessions with a pregnancy care provider offer a safe space where you can openly express your feelings. A trained professional understands what you’re going through and can help you navigate the complex emotions associated with miscarriage. They provide coping strategies to support your healing process.
Support groups allow you to connect with others who have had similar experiences. Sharing your story, listening to others, and knowing that you’re not alone can be incredibly therapeutic. These groups often provide a sense of community and understanding that can aid in the healing journey.
Taking time off work or reducing stress levels can contribute to physical and emotional healing.
After experiencing a miscarriage, it’s important to prioritize self-care and give yourself time to heal both physically and emotionally. Taking time off work or reducing your workload temporarily can alleviate stress and allow you to focus on your well-being.
Stress reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in activities that bring you joy can also be beneficial. It’s crucial to listen to your body and give yourself permission to rest when needed.
Discussing future pregnancy plans with healthcare providers for guidance is essential.
If you’re planning on trying for another pregnancy after a miscarriage, it’s essential to have open discussions with your healthcare provider about your options and any concerns you may have. They can provide guidance tailored to your specific situation, taking into account any underlying conditions that may have contributed to the miscarriage.
Your healthcare provider will evaluate factors such as age, medical history, previous pregnancies, and potential risk factors before providing recommendations. They may suggest additional testing or interventions depending on your individual circumstances.
By working closely with your healthcare provider, you can make informed decisions about family planning while addressing any potential underlying conditions that may impact future pregnancies.

Trying to Conceive After Miscarriage: Timing and Fertility Considerations
Waiting for one menstrual cycle after a miscarriage before trying again is often recommended.
After experiencing a miscarriage, it’s natural to feel eager and hopeful about getting pregnant again. However, it’s important to give your body time to heal both physically and emotionally. Many healthcare professionals recommend waiting for at least one menstrual cycle before attempting another pregnancy. This allows the uterus to fully recover and ensures that the lining is ready for implantation.
While waiting for your next menstrual cycle, take this time to focus on self-care. Allow yourself space to grieve and process the loss you’ve experienced. It can be helpful to lean on supportive friends, family members, or even seek professional counseling if needed. Remember that everyone’s healing journey is unique, so listen to your body and emotions as you navigate this sensitive time.
Understanding ovulation patterns and timing intercourse accordingly can increase chances of conception.
Once you’re ready to try conceiving again, understanding your ovulation patterns becomes crucial. Ovulation is the release of an egg from the ovaries, which typically occurs around the middle of your menstrual cycle. By tracking your menstrual cycles and monitoring signs such as changes in cervical mucus or using ovulation predictor kits, you can identify when you are most fertile.
Timing intercourse during your fertile window significantly increases the chances of fertilization taking place. Sperm can survive in the reproductive tract for up to five days, while an egg remains viable for about 24 hours after ovulation. Therefore, having regular intercourse every two to three days leading up to ovulation maximizes the probability of sperm being present at the right time for fertilization.
Seeking fertility evaluations if experiencing recurrent miscarriages may be beneficial.
Experiencing multiple miscarriages can be emotionally devastating and raise concerns about underlying fertility issues. If you have had two or more consecutive miscarriages, it may be beneficial to seek a fertility evaluation. This involves comprehensive testing for both partners to identify any potential factors contributing to recurrent pregnancy loss.
During the evaluation, your healthcare provider will assess various aspects such as hormonal imbalances, genetic abnormalities, uterine abnormalities, or issues with sperm quality. Understanding the underlying causes can help guide treatment options and increase the chances of a successful pregnancy in the future. Remember that seeking professional guidance and support is essential during this process.
Lifestyle changes like maintaining a healthy weight and managing stress can improve fertility outcomes.
While there are many factors that contribute to fertility, certain lifestyle changes can positively impact your chances of conceiving after a miscarriage. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial as both underweight and overweight conditions can affect hormone levels and disrupt ovulation.
Managing stress plays a significant role in fertility outcomes. High levels of stress can interfere with hormone production and menstrual regularity. Incorporating relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy can help reduce stress levels and promote overall well-being.
Support from partners, friends, or professionals can help navigate the emotional journey of trying again.
Trying to conceive after experiencing a miscarriage can be an emotional rollercoaster. It’s important to surround yourself with supportive individuals who understand your journey and provide comfort along the way. Your partner’s support is particularly crucial during this time as you navigate through mixed emotions together.
Seeking support from friends who have gone through similar experiences or joining online communities dedicated to pregnancy after loss can also provide valuable insights and encouragement. Professional counseling or therapy sessions offer a safe space to express your feelings openly and receive guidance on coping strategies specific to your situation.
Remember that every person’s healing process is unique, so be patient with yourself as you embark on this new chapter of trying again for a baby.

Genetic and Chromosome Issues: Implications for Miscarriage Risk
Genetic and chromosome issues play a significant role in the risk of miscarriage. Let’s delve into some key points regarding this topic:
Chromosomal abnormalities are the leading cause of early pregnancy loss.
Chromosomal abnormalities take center stage as the primary culprit. These abnormalities occur when there are errors or changes in the number or structure of chromosomes in the embryo. The most common chromosomal abnormality associated with miscarriage is called aneuploidy, which refers to an abnormal number of chromosomes.
Aneuploidy can lead to severe developmental problems in the fetus, making it difficult for it to survive. It is estimated that around 50-60% of first-trimester miscarriages result from chromosomal abnormalities. These abnormalities often occur randomly during fertilization and are not typically related to any specific actions or behaviors on the part of the parents.
Advanced maternal age increases the likelihood of chromosomal issues in embryos.
As women age, their eggs become more susceptible to developing chromosomal abnormalities. This means that advanced maternal age can significantly increase the risk of miscarriage due to genetic factors. As a woman gets older, her eggs may have a higher chance of having an incorrect number of chromosomes or structural defects.
The chance of having a pregnancy affected by chromosomal issues rises notably after the age of 35. This is why women who plan on conceiving later in life should be aware that they might face an increased risk of miscarriage due to genetic factors.
Inherited genetic disorders from either parent can contribute to an increased risk of miscarriage.
Apart from random occurrences during fertilization and advanced maternal age, inherited genetic disorders can also contribute to an increased risk of miscarriage. If either parent carries a gene mutation responsible for a genetic disorder, there is a possibility that their child may inherit this condition.
Certain genetic disorders can negatively impact the development of the fetus, making it more vulnerable to miscarriage. It is essential for couples who have a family history of genetic disorders to consult with a healthcare professional or genetic specialist before planning a pregnancy. They can provide guidance on potential risks and discuss available options for managing these risks.
Prenatal genetic testing options such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS) are available for assessing chromosomal health during pregnancy.
During pregnancy, certain prenatal genetic testing options are available to assess the chromosomal health of the developing fetus. Two common procedures used for this purpose are amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
Amniocentesis involves extracting a small amount of amniotic fluid from around the fetus and analyzing it for any chromosomal abnormalities. On the other hand, CVS involves taking a sample of cells from the placenta and examining them for genetic issues.
These tests can help identify whether there are any significant chromosomal abnormalities present in the fetus, giving parents valuable information about their pregnancy’s health. However, it’s important to note that these tests carry some risks, such as a slight chance of miscarriage due to their invasive nature. Therefore, it is crucial for expectant parents to discuss these options thoroughly with their healthcare provider before deciding whether or not to proceed with prenatal genetic testing.
Counseling with a genetic specialist may be recommended for couples at higher risk.
For couples at higher risk of miscarriage due to genetic factors, seeking counseling with a genetic specialist can be beneficial. These specialists have expertise in evaluating family medical histories and identifying potential risks associated with inherited conditions.
Genetic counselors can provide personalized advice based on an individual or couple’s specific circumstances. They can help explain complex concepts related to genetics, discuss available screening options, and guide decision-making regarding family planning.

Insights into Miscarriage Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
Now let’s summarize the key points and provide some important takeaways.
Causes of Miscarriage: Exploring Risk Factors
Miscarriages can occur due to a variety of reasons. Some common risk factors include advanced maternal age, certain medical conditions (such as diabetes or thyroid disorders), hormonal imbalances, genetic abnormalities in the fetus, uterine abnormalities, infections, and lifestyle factors like smoking or excessive alcohol consumption.
Signs and Symptoms: Recognizing Early Warning Signs
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a miscarriage is crucial for seeking timely medical attention. These may include vaginal bleeding (ranging from light spotting to heavy bleeding), abdominal pain or cramping, passing tissue or clots from the vagina, sudden decrease in pregnancy symptoms (such as breast tenderness or morning sickness), and back pain.
Diagnosing Miscarriage: Tests and Procedures
To diagnose a miscarriage accurately, healthcare professionals may perform various tests and procedures. These can include ultrasound scans to check for fetal heartbeat or growth abnormalities, blood tests to measure hormone levels (like human chorionic gonadotropin – hCG), pelvic exams to assess the cervix’s condition or any signs of infection.
Treatment Options: Addressing Emotional and Physical Needs
The treatment approach for miscarriage depends on several factors such as gestational age, severity of symptoms, personal preferences, and overall health. In some cases where the body naturally expels all pregnancy tissues without complications (known as spontaneous abortion), no further intervention may be necessary except emotional support. However, medical management with medications or surgical procedures like dilation & curettage (D&C) may be recommended if incomplete miscarriage or complications arise.
Trying to Conceive After Miscarriage: Timing and Fertility Considerations
After experiencing a miscarriage, it is natural to have concerns about future pregnancies. While the decision to try again varies from person to person, it’s generally advised to wait until you have physically and emotionally recovered. Discussing with your healthcare provider can help determine when it’s safe for you to conceive again. They may suggest certain lifestyle changes or fertility treatments if needed.
Genetic and Chromosome Issues: Implications for Miscarriage Risk
Genetic abnormalities in the fetus are one of the leading causes of miscarriage. Some individuals may carry genetic mutations that increase their risk of having a miscarriage. Genetic counseling and testing can provide valuable insights into these risks, helping individuals make informed decisions about family planning and potential interventions.
In conclusion, understanding the various aspects of miscarriage diagnosis, treatment, and prevention is essential for anyone who has experienced or is at risk of experiencing a miscarriage. By recognizing early warning signs, seeking timely medical attention, discussing treatment options with healthcare professionals, considering fertility factors after a miscarriage, and addressing genetic implications, individuals can take proactive steps towards their reproductive health.

FAQs
Q1: Can stress cause a miscarriage?
Stress alone does not directly cause a miscarriage. However, excessive stress can potentially impact overall health and well-being during pregnancy. It is important to manage stress levels through self-care practices like relaxation techniques or seeking support from loved ones.
Q2: Is there anything I can do to prevent a miscarriage?
While some risk factors are beyond our control (such as age or genetic factors), maintaining a healthy lifestyle by avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, managing chronic conditions effectively (like diabetes), getting regular prenatal care check-ups, and following medical advice can help reduce the risk of miscarriages.
Q3: How long does it take to recover emotionally after a miscarriage?
The emotional recovery process varies for each individual. It is normal to experience a range of emotions such as grief, sadness, anger, or guilt. Give yourself time and space to heal, and consider seeking support from healthcare professionals, support groups, or loved ones who can provide understanding and empathy.
Q4: Are there any alternative treatments for miscarriage?
While medical management or surgical procedures are the standard treatment options for miscarriages, some individuals may explore complementary therapies like acupuncture or herbal remedies. However, it’s important to consult with healthcare professionals before trying any alternative treatments to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Q5: When can I start trying to conceive again after a miscarriage?
The timing for trying to conceive again after a miscarriage varies depending on individual circumstances. Generally, healthcare providers recommend waiting until you have physically recovered and have had at least one menstrual cycle. However, it’s essential to discuss this with your healthcare provider who can provide personalized guidance based on your specific situation.
Q6: How common are recurrent miscarriages?
Recurrent miscarriages (experiencing three or more consecutive pregnancy losses) occur in about 1-2% of couples trying to conceive. If you have experienced recurrent miscarriages, it is crucial to seek medical evaluation as underlying factors like genetic issues or hormonal imbalances could be contributing factors that require specialized care.