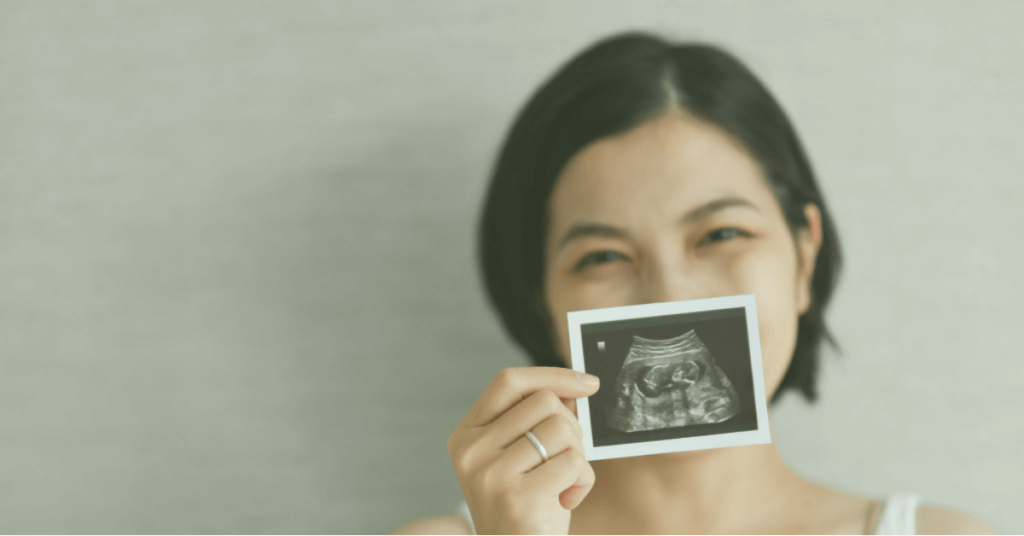
Bad egg quality is a term used to describe eggs that are not healthy or have poor quality. Poor quality eggs can affect fertility and the ability to conceive, making it essential to understand the signs of bad egg quality. Egg quality is determined by various factors such as age, genetics, and environmental factors. Reproductive aging can also impact egg quality, which is why it’s crucial to take care of your fertile soul. Healthy eggs are crucial for successful fertilization and embryo development, especially when undergoing reproductive medicine treatments. High FSH levels can also be an indicator of poor egg quality.
Egg quantity does not necessarily indicate egg quality, which can lead to fertility challenges for those trying to conceive. Women may still produce a significant number of eggs but with poor quality, resulting in difficulty achieving overall fertility and a healthy pregnancy. Knowing the signs of bad egg quality can help individuals trying to conceive identify potential issues early on and increase their chances of a successful pregnancy.
One sign of bad egg quality is related to reproductive aging. As women age, their ovaries produce fewer high-quality eggs, leading to fertility challenges and reducing their chances of overall fertility and healthy pregnancy. Genetic factors can also affect egg health and lead to poor-quality eggs.
Environmental factors such as smoking and alcohol consumption, exposure to toxins or radiation can also negatively impact egg health, which in turn affects reproductive aging and overall fertility. It is important to note that nourishment plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of the reproductive system. These harmful substances can damage the DNA within the eggs and impair their ability to develop into healthy embryos.
Another sign of bad egg quality is irregular menstrual cycles or ovulation patterns, especially in women with advanced maternal age or high FSH levels. These abnormalities can lead to abnormal eggs and affect overall reproductive health, making it difficult for even the most fertile soul to conceive.
Women who experience multiple failed IVF cycles may also be experiencing issues with poor-quality eggs, which could be due to advanced maternal age or overall fertility. Additionally, factors such as a fertile soul and proper blood flow to the reproductive organs can also play a crucial role in egg quality. This could be impacted by underlying medical conditions such as endometriosis or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Causes of Poor Egg Quality: Age and Genetic Abnormalities
Reproductive aging is a natural process that occurs as women get older, affecting their overall fertility. As a result, poor egg quality may be caused by this process. Advanced maternal age, typically defined as over 35 years old, is a well-known risk factor for poor egg quality and can affect the cycle. However, maternal age and cycle are not the only factors that affect egg quality; genetic abnormalities and other environmental factors can also play a role. It is important to remember that with wisdom comes an understanding of how our body changes over time, and seeking medical advice can help address any concerns about reproductive health.
As women age, they tend to have more small follicles in their ovaries, which can lead to decreased egg quality. These small follicles are often called “resting” or “dormant” follicles because they are not actively producing eggs. When these follicles start to grow again after being dormant for some time, they may produce eggs with chromosomal abnormalities or other defects. The cycle of these follicles is closely linked to the blood flow and system in the ovary.
Genetic abnormalities can also contribute to poor egg quality. For example, certain genetic mutations can cause premature ovarian failure (POF), which leads to an early menopause and reduced fertility. Other genetic mutations can affect the way eggs develop and mature in the ovaries, leading to abnormal chromosomes and decreased fertility.
While there are some treatments available to improve normal egg quality, such as fertility drugs and in vitro fertilization (IVF), these options may not be effective for all women. Fertility drugs work by stimulating the ovaries to produce more normal eggs each cycle; however, this does not necessarily improve the quality of those normal eggs. IVF involves retrieving normal mature eggs from the ovaries and fertilizing them outside of the body before transferring them back into the uterus; however, this procedure cannot correct underlying issues with normal egg quality.
Ultimately, the best way to improve egg quality is to take steps to maintain overall reproductive health throughout your life. This includes eating a healthy diet rich in antioxidants and avoiding toxins such as cigarette smoke and alcohol; exercising regularly; managing stress levels; getting regular check-ups with your healthcare provider, and reducing the risk of abnormal eggs.
Symptoms of Bad Egg Quality: Irregular Menstrual Cycles and Miscarriages
Irregular menstrual cycles can be a symptom of bad egg quality. the health and quality of a woman’s eggs are paramount. Irregular periods can be an indication that something is off with the reproductive system. Women who experience irregular cycles may have difficulty conceiving or have an increased risk of miscarriage.
The ovaries play a crucial role in egg quality, and medical conditions affecting the ovaries can impact egg quality. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is one such condition that affects up to 10% of women of childbearing age. PCOS disrupts normal ovulation, leading to irregular periods and reduced egg quality, including abnormal eggs. Endometriosis is another condition that affects the ovaries and can cause infertility, potentially leading to abnormal eggs.
Abnormal eggs can result from genetic abnormalities or damage to the eggs during development. The older a woman gets, the more likely she is to produce abnormal eggs due to natural aging processes in the body. However, certain lifestyle factors like smoking and exposure to toxins can also damage eggs, leading to a decrease in good quality.
Many women with bad egg quality may experience heavier or lighter periods, or periods that last for more or fewer days than usual. Changes in menstrual flow could indicate hormonal imbalances that affect ovulation and egg quality.
Blood tests and ultrasounds can help diagnose issues with egg quality, but it may take several months of testing to determine the cause. A blood test called anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) measures ovarian reserve – how many viable follicles remain in the ovaries – which gives an indication of egg quantity and therefore potential fertility. Ultrasound scans can detect any abnormalities in the uterus or ovaries that could be impacting fertility.

Diagnostic Tests for Egg Quality: Ovarian Reserve Testing and AMH Screening
If you’re trying to conceive, it’s important to understand the quality of your eggs. Diagnostic tests for egg quality include ovarian reserve testing and AMH screening. These tests can help diagnose low egg reserve, which is a common cause of infertility.
Ovarian Reserve Testing
Ovarian reserve testing measures the number of antral follicles in the ovary. Antral follicles are small fluid-filled sacs that contain immature eggs. By counting these follicles, doctors can estimate how many eggs a woman has left in her ovaries. This information can be used to predict how well a woman will respond to fertility treatments.
Low Egg Reserve Diagnosis
Low egg reserve can be diagnosed through antral follicle count and AMH level tests. FSH and estradiol levels can also be used to diagnose low egg reserve. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is produced by the pituitary gland and helps regulate the menstrual cycle and ovulation. High levels of FSH may indicate that a woman has fewer eggs than normal. Estradiol is a form of estrogen that is produced by the ovaries. Elevated levels of estradiol may also indicate low egg reserve.
AMH Level Test
Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels are a reliable indicator of ovarian reserve. AMH is produced by cells in developing ovarian follicles, so high levels suggest that a woman has more eggs remaining in her ovaries than someone with lower levels.
Treatment Options for Bad Egg Quality: Lifestyle Changes and Infertility Treatments
Lifestyle Changes for Improved Egg Quality
Maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine is crucial for improving egg quality. A balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can provide the necessary nutrients to support ovarian function and egg development. Regular exercise can also improve blood flow to the ovaries and reduce stress levels, which can have a positive impact on fertility.
In addition to these lifestyle changes, certain vitamins and supplements may also be recommended to improve egg quality. Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is an antioxidant that plays a key role in energy production within cells. It has been shown to improve ovarian response and increase the number of mature eggs retrieved during IVF cycles. Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) is another supplement that has been found to improve egg quality in women over 40 by increasing estrogen production.
Infertility Treatments for Bad Egg Quality
For women with poor egg quality who are struggling to conceive naturally, there are several infertility treatments available that can help increase their chances of success.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) with preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) is one option that can help identify and select the healthiest embryos for implantation, especially for those who have difficulty producing healthy eggs. PGT involves taking a small sample of cells from each embryo created through IVF and analyzing them for chromosomal abnormalities or genetic diseases before transferring them into the uterus. This technique can significantly increase pregnancy rates while reducing the risk of miscarriage or birth defects, particularly in cases of poor quality eggs.
Egg donation is another option for women with poor egg quality who want to conceive. This involves using donor eggs from a young, healthy woman who has undergone ovarian stimulation and retrieval procedures similar to those used in IVF. The donor eggs are then fertilized with sperm from the recipient’s partner or a sperm donor before being transferred into the recipient’s uterus.
Consultation with a fertility specialist is essential when considering treatment options for bad egg quality. They can conduct a thorough evaluation to determine the underlying causes of infertility and recommend the most appropriate course of action based on individual circumstances.
Medical Treatments for Bad Egg Quality: Clomiphene Citrate Challenge Test and IVF
Clomiphene Citrate Challenge Test (CCCT) and IVF Treatment for Bad Egg Quality
Clomiphene Citrate Challenge Test (CCCT) is a medical treatment that evaluates ovarian reserve and predicts response to IVF treatment. It involves taking clomiphene citrate, a medication that stimulates the ovaries to produce more eggs, followed by blood tests to measure hormone levels. The results of this test can help doctors determine the best course of action for women with bad egg quality.
IVF treatment is an effective option for women with bad egg quality, especially those with high FSH levels. During IVF, eggs are retrieved from the ovaries and fertilized in a laboratory before being implanted into the uterus. This process can be customized to fit the specific needs of each patient, including the use of donor eggs.
IVF protocols can be tailored to increase the chances of success for women with bad egg quality. For example, some patients may benefit from using higher doses of medications or undergoing multiple rounds of IVF. Doctors may recommend using donor eggs if a patient’s own eggs have poor quality or low quantity.
Donor eggs can provide a higher chance of success for women with bad egg quality who are unable to conceive with their own eggs. Donor eggs come from young and healthy donors who undergo rigorous screening processes to ensure their suitability as donors. Using donor eggs during IVF has been shown to significantly improve pregnancy rates and live birth rates compared to using a woman’s own poor-quality eggs.
Overcoming Infertility with Bad Egg Quality Treatment Options
Medical Treatment Options for Bad Egg Quality Infertility
Infertility is a common problem that affects many couples worldwide. One of the leading causes of infertility in women is bad egg quality. Fortunately, medical science has developed several treatment options to help women with this condition conceive and have healthy babies.
Hormone Therapy
One of the most common treatment options for bad egg quality infertility is hormone therapy. Hormones such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) are used to stimulate the ovaries to produce more eggs. This treatment can be administered orally or through injections.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
Another popular treatment option for bad egg quality infertility is in vitro fertilization (IVF). IVF involves extracting mature eggs from a woman’s ovaries and fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory dish. The resulting embryos are then implanted into the woman’s uterus.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is another medical treatment option for bad egg quality infertility. This procedure involves injecting a single sperm directly into an egg to fertilize it. ICSI is often used when male factor infertility is also present.
Egg Freezing
For women who want to preserve their eggs for future use, egg freezing is an option. This process involves harvesting healthy eggs from a woman’s ovaries and freezing them until they are needed. Egg freezing can be done at any age but yields better results when done before the age of 35.
Herbal Formulas
Herbal formulas have been used in traditional medicine to improve fertility, including bad egg quality infertility. However, their effectiveness has not been scientifically proven, making them less reliable than medical treatments.
Consulting with a Fertility Specialist
It is essential to consult with a fertility specialist to determine the best treatment option for individual cases. Factors such as age, overall health, and the severity of bad egg quality can affect the success rates of infertility treatments. A fertility specialist can help individuals understand their options and provide guidance on the best course of action.
Maintaining Perspective with Fertility Treatments
Dealing with infertility, especially due to poor quality eggs, can be a challenging and emotional journey. Fertility treatments are often viewed as the solution to this problem, but it’s important to maintain perspective and focus on the end goal of a successful pregnancy. Here are some things to consider when pursuing fertility treatments.
Consulting with a fertility specialist or reproductive endocrinologist can provide valuable insights into overall fertility and reproductive health, as well as options for assisted reproductive technologies like IVF. These specialists can help identify any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to infertility and recommend appropriate treatment options. By working closely with a specialist, individuals can gain a better understanding of their fertility status and make informed decisions about how best to proceed.
Hormone levels, particularly FSH levels, can provide important information about the growth phase of eggs and overall reproductive health. High FSH levels may indicate diminished ovarian reserve or poor egg quality. This information can guide treatment decisions and help manage expectations regarding the likelihood of success.
Taking steps to support reproductive health is also important in improving chances for successful fertilization and healthy pregnancy. This includes taking folic acid supplements, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, managing stress levels, and getting enough sleep.
While fertility treatments can be a helpful tool for those struggling with conception, it’s important to remember that they are not a guarantee and should be approached with realistic expectations. Success rates vary depending on several factors such as age, underlying medical conditions, previous pregnancy history, etc.
Chromosomal Abnormalities and Miscarriage: The Impact on Fertility
Fertility challenges are a common concern for many couples trying to conceive. While there are numerous factors that can affect fertility, chromosomal abnormalities in eggs can be a significant contributor. In this section, we will discuss how chromosomal abnormalities impact fertility and the likelihood of miscarriage.
Chromosomal Abnormalities Can Lead to Fertility Challenges
Chromosomes carry genetic information that determines physical traits and characteristics. When an egg is fertilized by sperm, the resulting embryo should have 46 chromosomes – 23 from each parent. However, sometimes errors occur during cell division that result in an incorrect number of chromosomes in the egg or sperm. This is known as a chromosomal abnormality.
When an embryo has too few or too many chromosomes, it often results in developmental issues that can lead to infertility or miscarriage. For example, Down syndrome is caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21 and is associated with intellectual disability and other health problems.
Miscarriage Is a Common Result of Chromosomal Abnormalities in Eggs
Miscarriage occurs when a pregnancy ends before the 20th week. Chromosomal abnormalities are estimated to cause up to 70% of all first-trimester miscarriages. Women with poor egg quality are at higher risk for miscarriage due to increased likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities.
The Likelihood of Chromosomal Abnormalities Increases With Age
A woman’s age is one of the most significant factors affecting egg quality and the likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities. As women age, their eggs accumulate genetic mutations and damage that can lead to developmental issues in embryos.
For example, women under 35 have about a 15-20% chance of having a baby with Down syndrome if they conceive naturally. However, this risk increases significantly with age – at age 40, the risk jumps to around 1 in 100.
Fertility Treatments May Not Be Effective for Women With Poor Egg Quality and Chromosomal Abnormalities
For couples struggling with infertility, fertility treatments like in vitro fertilization (IVF) can be an effective option. However, these treatments may not be as successful for women with poor egg quality and chromosomal abnormalities.
During IVF, eggs are collected from the woman and fertilized in a lab before being implanted in the uterus. If the eggs have chromosomal abnormalities, it can lead to failed implantation or miscarriage. The success rates of IVF decrease significantly for women over 35 due to age-related decline in egg quality.
Taking Action Against Bad Egg Quality
In conclusion, bad egg quality can be a challenging problem for those trying to conceive. Age and genetic abnormalities are the leading causes of poor egg quality, and symptoms such as irregular menstrual cycles and miscarriages can indicate a potential issue. However, there are diagnostic tests available that can help assess ovarian reserve and AMH screening.
If you have been diagnosed with bad egg quality, there are several treatment options available. Lifestyle changes such as improving your diet and exercise routine can make a significant impact on your fertility. Infertility treatments such as Clomiphene Citrate Challenge Test and IVF may also be helpful in overcoming infertility caused by bad egg quality.
It is essential to maintain perspective throughout the fertility treatment process. The emotional toll of infertility can be overwhelming, but it is crucial to remain optimistic and hopeful about the possibilities of conception. It is also important to understand the impact that chromosomal abnormalities can have on fertility and miscarriage rates.