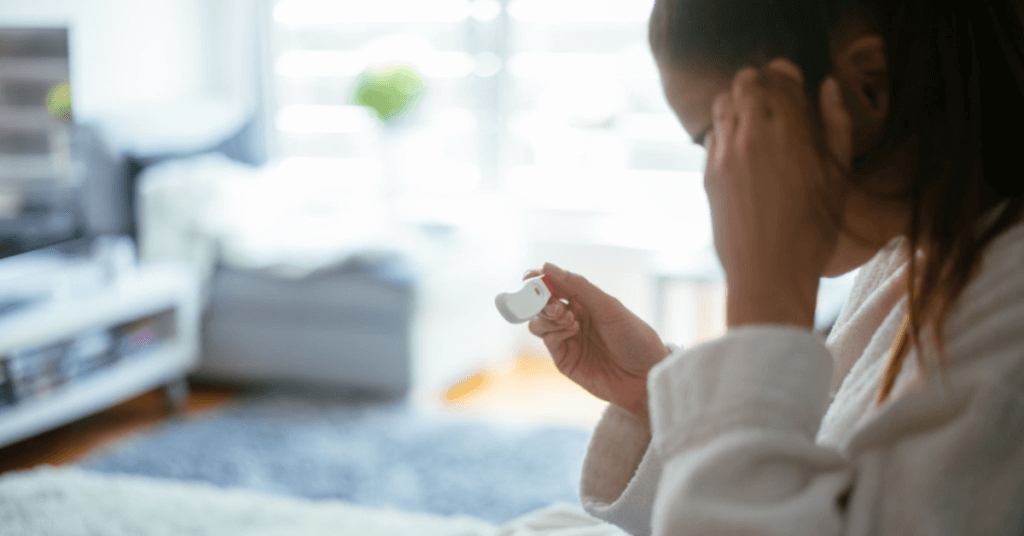
Have you been trying to conceive for years without any luck? Are you wondering what could be causing your inability to get pregnant? You may be experiencing female infertility, a condition where a woman has difficulty conceiving or carrying a pregnancy to term. This could be due to irregular periods, abnormal ovulation, fallopian tube blockages or tubal disease.
Infertility affects approximately 10% of women in the United States alone. While it can be frustrating and emotionally draining, understanding the common causes of female infertility such as abnormal ovulation, tubal disease, irregular periods, and low pregnancy rates can help you take steps towards finding a solution.
Hormonal imbalances, ovulation disorders, and irregular periods, as well as structural problems such as tubal disease and abnormalities in the uterine cavity, are some of the most common causes of female infertility. In some cases, despite extensive testing and evaluation, the exact cause of infertility remains unexplained, while in other cases, multiple fetuses can also contribute to difficulties in conception.
Infections, diseases, and other medical conditions, as well as unexplained infertility and female factors, can also contribute to fertility problems in women. It is important to consider your medical history and journal any symptoms or conditions that may affect your ability to conceive, including abnormal ovulation and health information.
If you have been trying to conceive for over a year without success (or six months if you are over 35), it is important to seek medical attention from doctors. A doctor will evaluate your case and run tests to determine if there are any underlying female factors or tubal disease causing your infertility. They will also check for abnormal ovulation to ensure that there are no complications in the process.
We will explore both common and uncommon causes of infertility while providing information on how you can improve your chances of having a child. Patients with womb-related disease may find this particularly helpful. Additionally, Mayo Clinic offers valuable resources on the topic.
So let’s cut to the chase – what exactly is female infertility? It is a condition that affects a woman’s ability to conceive and carry a pregnancy to term due to issues with her womb, tubes, or diseases. Doctors often diagnose female infertility after conducting several tests and examinations.

Risk Factors for Female Infertility
Female infertility is a complex issue that can be caused by various factors. The following are some risk factors that can contribute to fertility problems in women, including diseases affecting the womb. Patients should consult with their doctors for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Age
Age is one of the most significant risk factors for female infertility. As women age, their egg quality and quantity decrease, making it more challenging to conceive. Women over the age of 35, who have been diagnosed with a disease affecting their reproductive tube, are at a higher risk of fertility problems than younger patients. This decline in fertility is due to a natural process where the number and quality of eggs diminish as a woman ages, which requires the attention of doctors.
Health Conditions
Certain health conditions such as PCOS and endometriosis can cause female infertility, which can be a major concern for patients. These diseases can lead to hormonal imbalances, tissue growth outside the uterus, irregular periods, pain during intercourse and menstrual cycles. It is important for patients to seek information and consult with doctors to manage these conditions effectively.
Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices can also play a role in female infertility and disease. Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use have all been linked to decreased fertility in women. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and eating a nutritious diet has been shown to improve fertility outcomes. For more information on female infertility and disease, consult with your healthcare provider.
It’s important to note that infertility is not solely a female issue; male factors can also play a role in couples struggling to conceive. Male infertility may be caused by diseases, issues with sperm count or motility, among other factors.
Diagnosis of Female Infertility: Tests and Evaluations
There are a series of tests and evaluations that healthcare providers will perform to determine the underlying cause of infertility, which can help guide treatment options. These tests can also be used to diagnose any underlying disease that may be contributing to infertility.
Physical Exam and Medical History
The first step in diagnosing female infertility is typically a physical exam and medical history review. During this exam, your healthcare provider may ask about your menstrual cycle, sexual history, any previous pregnancies, and check for any signs of disease or infection during a pelvic exam.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are another common way to diagnose female infertility and related diseases. These tests can be used to check hormone levels, such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), estrogen, and progesterone, which can indicate issues with ovulation or other fertility-related problems and diseases.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the reproductive organs. This test can be used to check for structural abnormalities in the uterus or ovaries, such as cysts or fibroids. Ultrasound is also an effective tool in diagnosing unexplained infertility and detecting reproductive diseases. At Penn Fertility Care, we use ultrasound to provide comprehensive care for our patients.
Imaging Tests
In some cases, imaging tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans may be necessary to diagnose female infertility. These tests can provide more detailed images of the reproductive organs than an ultrasound.
Hysterosalpingogram (HSG)
A hysterosalpingogram (HSG) is a specialized type of X-ray offered at Penn Fertility Care that involves injecting dye into the uterus to check for blockages in the fallopian tubes. This test can help determine if there are any structural issues preventing conception from occurring naturally.
It’s important to note that some diagnostic tests require specific days of the menstrual cycle for accurate results. For example, blood tests may need to be performed on specific days to check hormone levels, and an HSG should be done after your period but before ovulation. If you’re seeking fertility care at Penn Fertility Care, our team will guide you through the process and ensure that all necessary tests are done at the appropriate times.
Time is a crucial factor. Early detection and treatment can improve the chances of successful conception. If you’ve been trying to conceive for over a year (or six months if you’re over 35), it’s time to see a doctor. Your healthcare provider can help determine what tests are necessary and guide you through the diagnosis process.
Uterine or Cervical Causes of Female Infertility
There are various factors that can contribute to the condition. One of the most common causes is abnormalities in the uterus or cervix.
Thick or Thin Cervical Mucus
Cervical mucus plays an essential role in fertility as it helps sperm reach the egg for fertilization. However, if the cervical mucus is too thick or too thin, it can hinder sperm from reaching the egg and decrease a woman’s chances of getting pregnant.
Thick cervical mucus can prevent sperm from penetrating through the cervix and into the uterus. This condition may be caused by certain medications, hormonal imbalances, infections such as chlamydia or gonorrhea, or even stress. On the other hand, thin cervical mucus may not provide enough protection for sperm during their journey towards fertilization.
If you suspect that your cervical mucus may be affecting your fertility, consult with your healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment options.
Abnormalities in the Uterine Cavity
The uterine cavity is where implantation occurs after fertilization takes place. Therefore, any abnormalities in this area can prevent a fertilized egg from attaching to its lining and growing into a healthy pregnancy.
Fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop within or around the uterus. Although most fibroids do not cause any symptoms, large ones located near the uterine cavity can interfere with implantation and lead to infertility.
Polyps are another type of growth that develops on the inner lining of the uterus. Like fibroids, polyps can also affect fertility by preventing implantation and increasing miscarriage risk.
Both fibroids and polyps can be diagnosed through imaging tests such as ultrasound or hysteroscopy. Treatment options may include medication, surgery, or a combination of both.
Structural Issues with the Uterus
Structural issues with the uterus can also interfere with implantation and pregnancy. For example, a uterine septum is a condition where the uterus is divided by a wall of tissue, which can decrease its size and affect blood flow to the developing fetus. Adhesions are another type of structural issue that occurs when scar tissue forms within the uterus, preventing implantation.
These conditions can be diagnosed through imaging tests such as MRI or hysteroscopy. Treatment options may include surgery to remove the septum or adhesions and improve fertility outcomes.
Infections or Inflammation
Infections or inflammation of the cervix or uterus can damage reproductive tissues and decrease fertility. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia or gonorrhea can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can lead to scarring and blockages in the fallopian tubes.
Endometritis is another type of infection that affects the lining of the uterus. This condition can lead to infertility by interfering with implantation and increasing miscarriage risk.
If you suspect that you may have an infection or inflammation in your reproductive system, seek medical attention promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Tubal Factor: A Major Cause of Female Infertility
What is Tubal Factor Infertility?
Tubal factor infertility is a common cause of female infertility, accounting for up to 35% of all cases. It occurs when the fallopian tubes, which are responsible for transporting the egg from the ovary to the uterus, become damaged or blocked. This can prevent fertilization and implantation of an egg, making it difficult or impossible for a woman to conceive.
Causes of Tubal Damage
There are several factors that can contribute to tubal factor infertility. One common cause is pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which is an infection in the reproductive organs that can lead to scarring and damage in the fallopian tubes. Other infections, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, can also cause inflammation and scarring in the tubes.
Endometriosis is another condition that can lead to tubal factor infertility. This occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside of the uterus, causing inflammation and scarring in nearby tissues including the fallopian tubes.
Previous surgeries involving the reproductive organs can also increase a woman’s risk for tubal factor infertility. Surgeries such as cesarean sections or surgeries to remove ovarian cysts or fibroids can cause adhesions and scar tissue that may block or narrow the fallopian tubes.
Effects of Tubal Damage on Fertility
When a woman has tubal factor infertility due to damage in her fallopian tubes, there are several ways this can affect her ability to conceive. The most obvious effect is that it can prevent sperm from reaching an egg for fertilization. If one or both tubes are blocked or narrowed, sperm may not be able to travel up into the tube where fertilization normally takes place.
Damage to the lining of the tube itself may make it more difficult for an egg to travel through the tube. The lining of the fallopian tubes is covered in tiny hair-like structures called cilia, which help move the egg towards the uterus. If these structures are damaged or destroyed, it can make it more difficult for an egg to reach its destination.
Finally, even if fertilization does occur, damage to the fallopian tubes can increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. This occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside of the uterus, often in one of the fallopian tubes. Ectopic pregnancies are dangerous and require immediate medical attention.
Treatment Options for Tubal Factor Infertility
The treatment options for tubal factor infertility depend on the severity and cause of the damage to the fallopian tubes. If there is only minor scarring or blockage, surgery may be an option to repair or open up the tubes.
In cases where surgery is not possible or effective, assisted reproductive technologies such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be recommended. IVF involves retrieving eggs from a woman’s ovaries and fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory setting. The resulting embryos are then transferred back into the woman’s uterus for implantation.
Another option is intrauterine insemination (IUI), which involves placing sperm directly into a woman’s uterus during ovulation. This can bypass any blockages or damage in the fallopian tubes and increase a woman’s chances of becoming pregnant.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and Female Infertility
What is PCOS?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. Women with PCOS have enlarged ovaries with small cysts on the outer edges. The hormonal imbalances caused by PCOS can disrupt the menstrual cycle and lead to infertility.
How does PCOS affect fertility?
PCOS is one of the leading causes of female infertility, affecting up to 10% of women of reproductive age. Women with PCOS may experience irregular periods or no periods at all, making it difficult to predict ovulation and conceive naturally. The hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS can interfere with the development and release of eggs from the ovaries.
Treatment options for women with PCOS
If you suspect you have PCOS and are struggling to conceive, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider or a fertility specialist like Penn Fertility Care. Depending on your individual situation, treatment options may include:
- Lifestyle changes: In some cases, making changes to your diet and exercise habits can help regulate hormone levels and improve fertility.
- Medications: Certain medications can be used to stimulate ovulation in women with PCOS.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF): If other treatments are unsuccessful, IVF may be recommended as a way to bypass issues related to ovulation and increase the chances of conception.
- Partner sperm donation: For women who do not have a male partner or whose partner has severe male factor infertility, donor sperm may be used in conjunction with other fertility treatments.
It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider or fertility specialist when deciding which treatment option is right for you.
Endometriosis and Female Infertility
What is endometriosis?
Endometriosis is a condition where the tissue that lines the uterus grows outside of it, causing pelvic pain and affecting fertility. This tissue, called the endometrium, can grow on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and other organs in the pelvic region. It can cause scarring and adhesions that can block the egg and sperm from meeting.
How does endometriosis affect fertility?
Women with endometriosis may experience irregular periods, ovulation problems, fibroids that can interfere with fertilization and implantation. The abnormal growth of endometrial tissues outside of the uterus can lead to inflammation in the pelvic area which affects fertility.
The inflammation caused by endometriosis can damage or block fallopian tubes making it difficult for sperm to reach an egg or for an egg to travel down into the uterus after ovulation. In some cases, if there is scarring or adhesions due to endometriosis around ovaries or fallopian tubes then it could result in infertility.
Endometriosis has also been linked to increased risk of miscarriage due to abnormal ovulation and egg production. Women with this condition are more likely to have multiple fetuses because their bodies may produce more than one egg during each menstrual cycle.
Treatment options for Endometriosis-related infertility
Treatment options for women with endometriosis-related infertility include surgery to remove the tissue, hormone therapy to regulate menstrual cycles, and assisted reproductive technologies like IVF (In Vitro Fertilization).
Surgery is often recommended when there are significant symptoms such as severe pain or heavy bleeding associated with endometriosis. During surgery doctors will attempt to remove as much of the affected tissue as possible while preserving healthy organs. This surgical procedure helps improve fertility by removing any blockages created by the tissue growth.
Hormone therapy is another treatment option for women with endometriosis-related infertility. Hormones such as birth control pills, progestin-only contraceptives, or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists can help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce pain associated with endometriosis. These medications work by suppressing estrogen production which helps to slow down the growth of endometrial tissues.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a fertility treatment that involves combining eggs and sperm outside of the body in a laboratory dish. The resulting embryos are then transferred into the uterus where they can implant and grow. Women with endometriosis who have not had success conceiving through other methods may consider IVF as an option.
Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (POI) and Female Infertility
What is Primary Ovarian Insufficiency?
Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) is a condition where the ovaries stop functioning normally before the age of 40. Women with POI have a reduced number of eggs in their ovaries, which can lead to infertility. POI used to be called premature ovarian failure or early menopause, but these terms are no longer used because they don’t accurately describe the condition.
Causes of Primary Ovarian Insufficiency
POI can be caused by a problem with the pituitary gland or an autoimmune disorder. The pituitary gland is responsible for producing hormones that stimulate the ovaries to produce estrogen and progesterone. If there’s a problem with the pituitary gland, it can disrupt this process and cause POI.
Autoimmune disorders occur when your immune system attacks healthy cells in your body by mistake. In some cases, the immune system may attack the ovaries and cause them to stop working properly.
Other causes of POI include genetic disorders, chemotherapy or radiation therapy for cancer treatment, and certain infections.
Diagnosing Primary Ovarian Insufficiency
If you suspect you have POI, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider and get a diagnosis. Your healthcare provider will likely perform blood tests to check your hormone levels and may recommend an ultrasound or other imaging tests to look at your ovaries.
It’s important to note that not all women with POI will experience symptoms right away. Some women may continue to have regular periods even though their ovaries aren’t functioning properly.
Treating Primary Ovarian Insufficiency
Treatment options for POI may include hormone therapy or assisted reproductive technologies (ART), but it’s important to pick the right option for your individual situation.
Hormone therapy involves taking estrogen and progesterone to replace the hormones that your ovaries are no longer producing. This can help alleviate symptoms of menopause and may also improve bone health.
ART involves using fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) to help you get pregnant. With IVF, eggs are removed from your ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory. The resulting embryos are then transferred to your uterus.
It’s important to note that ART is not always successful, and it can be expensive. Your healthcare provider can help you weigh the risks and benefits of each treatment option.
Medicines and Drugs for Treating Female Infertility
Hormones and Medications to Regulate Ovulation
For women experiencing infertility due to ovulation problems, doctors may prescribe medications that help regulate the menstrual cycle. These medicines work by stimulating the ovaries to produce eggs or by regulating hormone levels in the body.
One common medication used to induce ovulation is Clomiphene citrate, which is taken orally and helps stimulate the release of hormones necessary for ovulation. Another medication used to treat infertility is Gonadotropins, which are injected into the body and stimulate follicle growth in the ovaries.
It’s important to note that these medications can have side effects such as hot flashes, headaches, mood swings, and bloating. Multiple pregnancies can occur when using these medications, which can lead to complications during pregnancy.
Illegal Drugs and Their Impact on Fertility
Illegal drugs such as cocaine and marijuana have been shown to negatively impact fertility in women. Cocaine use can damage eggs within the ovaries while marijuana use can disrupt hormone levels needed for proper ovulation.
It’s important for women trying to conceive to avoid illegal drug use altogether. If you’re struggling with addiction or substance abuse issues, seek help from a healthcare provider before attempting conception.
Consult with a Healthcare Provider Before Taking Any Medication
Before taking any medication for infertility treatment, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider. They will determine if any underlying medical conditions need addressing before starting treatment and recommend appropriate medications based on your individual needs.
Some medications may interact negatively with other prescriptions or over-the-counter drugs you may be taking. A healthcare provider will advise you on what precautions need taking before beginning treatment.
Carriers Used for Delivering Medication Directly to Ovaries
In certain cases where traditional methods of medication administration are not effective enough at improving ovarian function, carriers may be used to deliver medication directly to the ovaries.
One example is intrauterine insemination (IUI), where sperm are placed directly into the uterus during ovulation. Another example is in vitro fertilization (IVF), which involves removing eggs from the ovaries and fertilizing them outside of the body before implanting them back into the uterus.
These methods can be costly and may not be covered by insurance, so it’s important to discuss all options with a healthcare provider before making any decisions.
Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) Options for Female Infertility Treatment
What is assisted reproductive technology (ART)?
Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) refers to a group of medical procedures that use reproductive technology to help women who have difficulty conceiving. ART has been a lifesaver for many couples struggling with infertility, and it offers hope where there was none before. The ART process involves the manipulation of eggs, sperm, and embryos outside the body to increase the chances of conception.
What are the different types of assisted reproductive technology (ART)?
There are several types of ART options available for female infertility treatment. These include:
- Artificial Insemination: This procedure involves injecting sperm directly into the uterus to increase the chances of fertilization. This option is ideal for women who have healthy fallopian tubes but whose partners have low sperm count or mobility issues.
- In vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF is a popular ART option where eggs are removed from the woman’s ovaries and fertilized in a lab before being implanted back into the uterus. This procedure is suitable for women with blocked fallopian tubes or those with endometriosis.
- Donor Eggs: In some cases, women may not be able to produce viable eggs due to age or underlying health conditions such as premature ovarian failure or genetic disorders. In such instances, donor eggs can be used instead.
- Surgery: Some ART procedures may involve surgery to retrieve eggs or correct any underlying reproductive issues that affect a woman’s ability to conceive.
How often is assisted reproductive technology (ART) successful?
The success rate of ART varies depending on several factors such as age, overall health status, type of procedure used, and underlying fertility issues. While some couples may achieve pregnancy after one cycle of treatment, others may require multiple attempts before they can conceive successfully.
According to statistics from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, the success rate of ART varies between 20-35% per cycle for women under 35 years and decreases with age. Women over 40 years have a lower chance of conceiving through ART due to a decrease in egg quality and quantity.
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) Process and Success Rates
What is Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)?
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a fertility treatment process that involves placing sperm directly into the uterus to increase the chances of fertilization. This process can be performed with the partner’s sperm or donor sperm, depending on the individual’s situation. IUI is typically used as a first-line treatment for couples experiencing unexplained infertility or male factor infertility.
IUI Process
The IUI process begins with monitoring ovulation through blood tests and ultrasounds. Once ovulation has been confirmed, a semen sample is collected from either the partner or a donor and washed to remove any impurities. The washed sperm is then placed into a catheter and inserted through the cervix into the uterus. The entire procedure takes only a few minutes and does not require anesthesia.
After the procedure, individuals may experience mild cramping or spotting. It is recommended to avoid strenuous activity for at least 24 hours after IUI. A pregnancy test can be taken approximately two weeks after the procedure to determine if it was successful.
Success Rates
The success rates of IUI vary depending on factors such as age, cause of infertility, and number of inseminations. On average, the pregnancy rate per cycle with IUI is around 10-20%. However, success rates can increase by performing multiple cycles of IUI.
Compared to in vitro fertilization (IVF), IUI has a lower success rate but is less invasive and less expensive. IVF success rates are generally higher but can cost up to $20,000 per cycle.
According to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the success rate of IUI in the United States ranges from 4% to 33%, depending on various factors such as age and cause of infertility. It is important to discuss with a healthcare provider to determine if IUI is the best option for an individual’s specific situation.
Available Treatments for Female Infertility
After identifying the possible causes of female infertility, it is crucial to explore the available treatments. The most appropriate treatment will depend on the underlying cause.
In some cases, lifestyle changes such as weight loss, reducing alcohol and caffeine intake, and quitting smoking can improve fertility. Medications like clomiphene citrate or letrozole can stimulate ovulation in women with ovulation disorders. Surgery may be necessary to correct uterine abnormalities or remove fibroids that are affecting fertility.
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) offers various options for women who cannot conceive naturally. Intrauterine insemination (IUI), where sperm is placed directly into the uterus during ovulation, has a moderate success rate and is less invasive than other ART procedures. In vitro fertilization (IVF), where eggs are retrieved from the ovaries and fertilized with sperm outside the body before being implanted in the uterus, has a higher success rate but is more invasive and expensive.
It’s important to note that not all treatments work for everyone and there is no guarantee of success. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine which option is best suited for your specific situation.
In conclusion, while female infertility can be caused by various factors, there are several available treatments depending on the underlying cause. Making lifestyle changes or taking medications may help improve fertility, while surgical procedures or assisted reproductive technology may be necessary in more severe cases. Consultation with a healthcare professional is vital in determining the most appropriate treatment plan for you.